Interpolation is a technique used to estimate unknown data points within a known range, aiming to create a smoother curve. Univariate interpolation specifically focuses on fitting a curve to a set of two-dimensional data points sampled from a single-variable function. This process enhances the continuity of the curve within the given range.
SciPy API provides several functions to implement the interpolation method for a given data. In this tutorial, you'll learn how to apply interpolation for a given data by using interp1d, CubicSpline, PchipInterpolator, and Akima1DInterplator methods in Python. The tutorial covers;- Preparing test data
- 1-D interpolation with interp1d
- CubicSpline method
- PchipInterpolator method
- Akima1DInterpolator method
- Source code listing
We'll start by loading the required libraries.
from scipy import interpolate
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np y = [-2,-1,-1,-2,-3,-1,-1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 6]
x = np.linspace(0, len(y), len(y))
plt.plot(x, y, '.r', markersize=10)plt.plot(x, y)plt.grid() plt.show()
An interp1d class finds the value of new points of one-dimensional function with a given method such as linear, nearest, cubic, and etc. The below listing shows implementation of interp1d method. First, we'll fit model on x and y data, then provide new x data to find out new estimated y values.
xnew = np.linspace(min(x), max(x), num=50) oned = interpolate.interp1d(x, y) yfit = oned(xnew) plt.plot(x, y, '.') plt.plot(xnew, yfit) plt.grid() plt.show()
CubicSpline uses a piecewise cubic polynomial that is twice continuously differentiable to interpolate data. The implementation of CubicSpline method is similar to above scripting.
oned = interpolate.CubicSpline(x, y) yfit = oned(xnew) plt.plot(x, y, '.') plt.plot(xnew, yfit) plt.grid() plt.show()
PCHIP (Piecewise Cubic Hermite Interpolating Polynomial) 1-D monotonic cubic interpolation employs monotonic cubic splines to determine the value of new points. The implementation of PchipInterpolator method is also similar to above scripting.
pchip = interpolate.PchipInterpolator(x, y) yfit = pchip(xnew) plt.plot(x, y, '.') plt.plot(xnew, yfit) plt.grid() plt.show()
Akima1DInterpolator fits piecewise cubic polynomials. Akima's interpolation method employs a continuously differentiable sub-spline constructed from piecewise cubic polynomials. The implementation of Akima1DInterpolator method is shown below.
akima = interpolate.Akima1DInterpolator(x, y) yfit = akima(xnew) plt.plot(x, y, '.') plt.plot(xnew, yfit) plt.grid() plt.show()
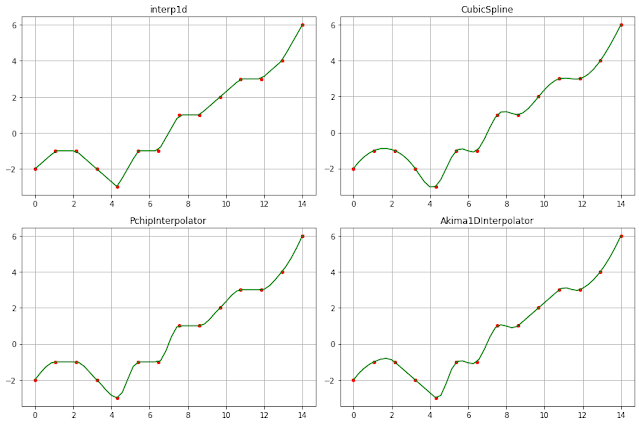
Finally, we put all together in one graph and compare each method performance with a given data. The following listing shows how to plot all in one graph.
# fit each method on x, y data
oned = interpolate.interp1d(x, y)
akima = interpolate.Akima1DInterpolator(x, y)
cubic = interpolate.CubicSpline(x, y)
pchip = interpolate.PchipInterpolator(x, y)
# create dictionary
funcs = {
oned:"interp1d",
cubic:"CubicSpline",
pchip:"PchipInterpolator",
akima:"Akima1DInterpolator" } # visualize in a graphi = 0
ig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize=(12, 8))
for row in range(2):
for col in range(2):
ax[row][col].plot(x, y, '.', c="g", markersize=8)
yfit = list(funcs.keys())[i](xnew)
ax[row][col].plot(xnew, yfit, 'r')
ax[row][col].set_title(list(funcs.values())[i])
ax[row][col].grid()
i = i + 1
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
from scipy import interpolate
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Preparing datay = [-2,-1,-1,-2,-3,-1,-1, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 6]
x = np.linspace(0, len(y), len(y))
plt.plot(x, y, '.r', markersize=10)plt.plot(x, y)plt.grid() plt.show()
xnew = np.linspace(min(x), max(x), num=50) # interp1d interpolation oned = interpolate.interp1d(x, y) yfit = oned(xnew) plt.plot(x, y, '.') plt.plot(xnew, yfit) plt.grid() plt.show()
# CubicSpline interpolation cubic = interpolate.CubicSpline(x, y) yfit = cubic(xnew) plt.plot(x, y, '.') plt.plot(xnew, yfit) plt.grid() plt.show()
# PchipInterpolator interpolation pchip = interpolate.PchipInterpolator(x, y) yfit = pchip(xnew) plt.plot(x, y, '.') plt.plot(xnew, yfit) plt.grid() plt.show()
# Akiam1DInterpolator interpolation akima = interpolate.Akima1DInterpolator(x, y) yfit = akima(xnew) plt.plot(x, y, '.') plt.plot(xnew, yfit) plt.grid() plt.show()
# fit each method on x, y data oned = interpolate.interp1d(x, y) akima = interpolate.Akima1DInterpolator(x, y) cubic = interpolate.CubicSpline(x, y) pchip = interpolate.PchipInterpolator(x, y) # create dictionary funcs = { oned:"interp1d", cubic:"CubicSpline", pchip:"PchipInterpolator", akima:"Akima1DInterpolator" }
# visualize in a graph
i = 0
ig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize=(12, 8))
for row in range(2):
for col in range(2):
ax[row][col].plot(x, y, '.', c="g", markersize=8)
yfit = list(funcs.keys())[i](xnew)
ax[row][col].plot(xnew, yfit, 'r')
ax[row][col].set_title(list(funcs.values())[i])
ax[row][col].grid()
i = i + 1
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()

No comments:
Post a Comment